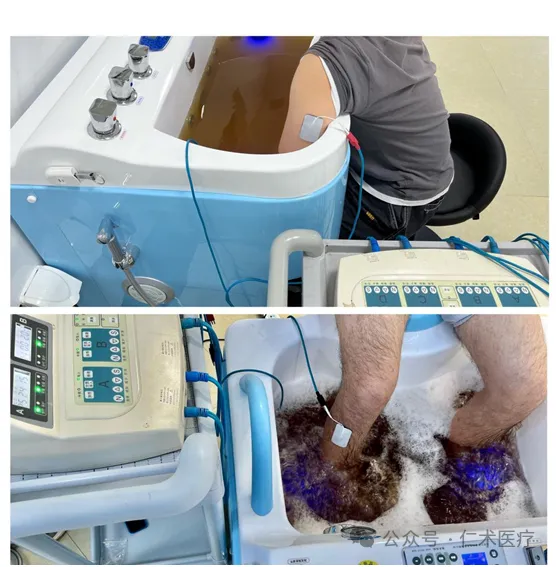
// Clinical Practical Hydrotherapy // Parkinson's Disease Water Treatment Rehabilitation
Release time:
2024-04-11
Parkinson's disease, also known as tremor paralysis, is a chronic, progressive degenerative disease of the central nervous system. The disease is characterized by resting tremor, myotonia, bradykinesia, and abnormal postural response.
Classification of Parkinson's disease
According to the etiology, Parkinson's disease can be divided into primary Parkinson's disease and secondary Parkinson's disease.
Secondary Parkinson's disease, also known as Parkinson's syndrome, mainly includes cerebrovascular Parkinson's syndrome, infectious Parkinson's syndrome, drug-induced Parkinson's syndrome and toxic Parkinson's syndrome. Parkinson's syndrome caused by stroke or craniocerebral injury is the indication of hydrotherapy. Using the unstable characteristics of the human body in the water, and cooperating with the hydrotherapy prescription designed by the hydrotherapist for the patient's condition, the balance and coordination function of the patient can be strengthened.
Clinical features of Parkinson's disease
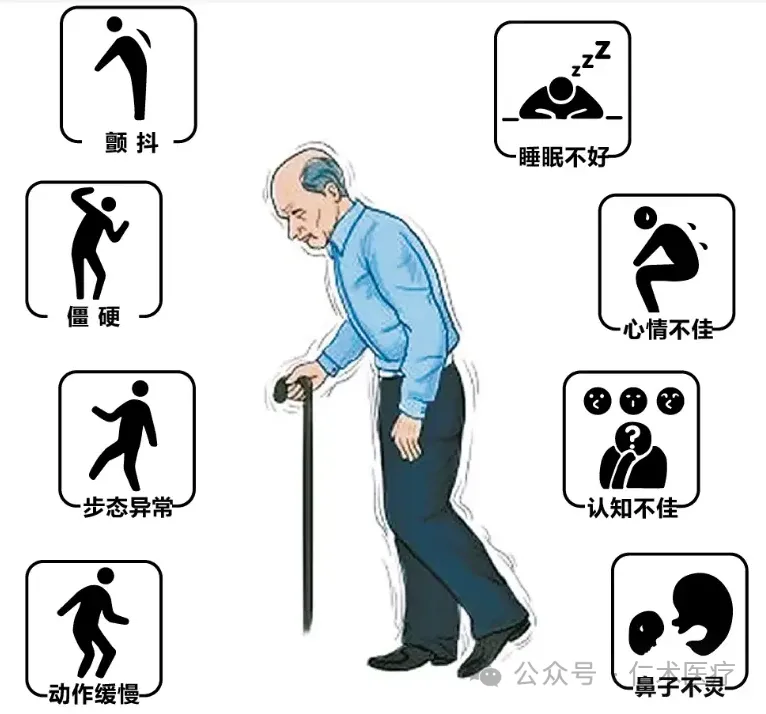
I) Slow movement and panic gait
Most of the clinical manifestations of patients start from a unilateral limb or a limb, with reduced movement and slow movement, difficulty in standing up after sitting for a long time, and difficulty in turning over, walking and walking. When walking, it stops slowly, and the upper limb swings are reduced, showing the typical panic gait of walking faster and faster.
(II) Muscle rigidity
The patient's muscles are in a state of rigidity, and the muscle tension increases when the limbs are moved. Due to the cheek muscle stiffness, resulting in facial dullness, the so-called "mask face".
(III) Resting tremor
Resting tremor is the first symptom in about one-third of patients with Parkinson's disease. This is due to the uncoordinated contraction of the muscles of the limbs, which leads to alternating contractions and causes rhythmic tremors in the limbs, usually 4-6 times/s. In the early stage, the tremor of the hand is more common; with the progress of the disease, the tremor can be extended to the lower limbs and the contralateral limbs; when the disease is serious, the tremor of the head, lips, tongue and jaw occurs.
Parkinson's disease Spa technology
First, the application of hydrotherapy rehabilitation technology in Parkinson's disease.
The symptoms of Parkinson's disease are not the same as the clinical symptoms of other diseases, which also leads to the difference between the treatment of Parkinson's disease and other diseases. However, in two special cases, supranuclear palsy and some types of multisystem degeneration have symptoms similar to those of Parkinson's disease. These symptoms are usually manifested by bradykinesia, rigidity (especially trunk), decreased movement, weakness of the trunk extensors of the limbs, decreased thoracic extension, and lack of postural and balance responses. Water treatment can improve these symptoms, because water has the effect of relieving stiffness, improving body retardation, promoting voluntary movement, and promoting full range of movement of limbs and trunk.
Second, Parkinson's disease water treatment rehabilitation operation method.
Taking water exercise therapy as an example, the hydrotherapy rehabilitation operation method of Parkinson's disease is listed.
(I) Torso rotation
1, the patient posture patients to take a standing position, feet apart, the distance between the two feet should be large enough to avoid losing balance, while the lower part of the body is stable and fixed, or the patient to take another posture, sitting in a chair, bilateral shoulder joint should be flat with the horizontal plane
2. Technical Methods The patient's bilateral shoulder joints abduction to below the horizontal plane (standing position or squatting position depending on the depth of the water), while maintaining the elbow joint extension, triggering the rotation of the trunk through the swing of the arm.

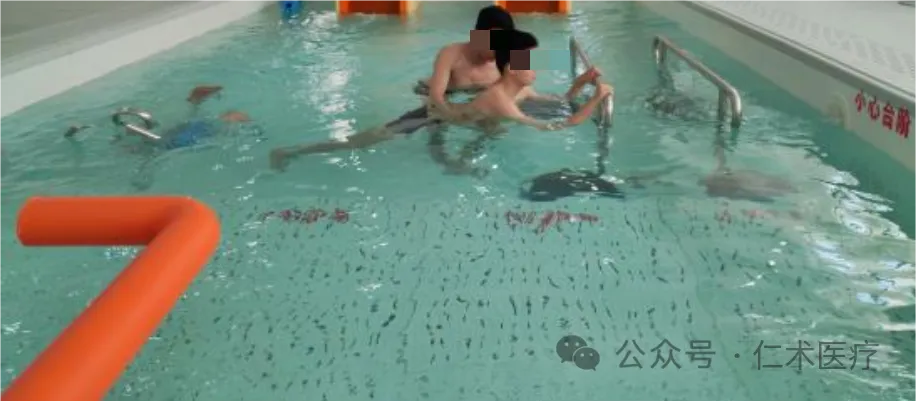
(II) Strength training of lower limbs and trunk extensor muscles
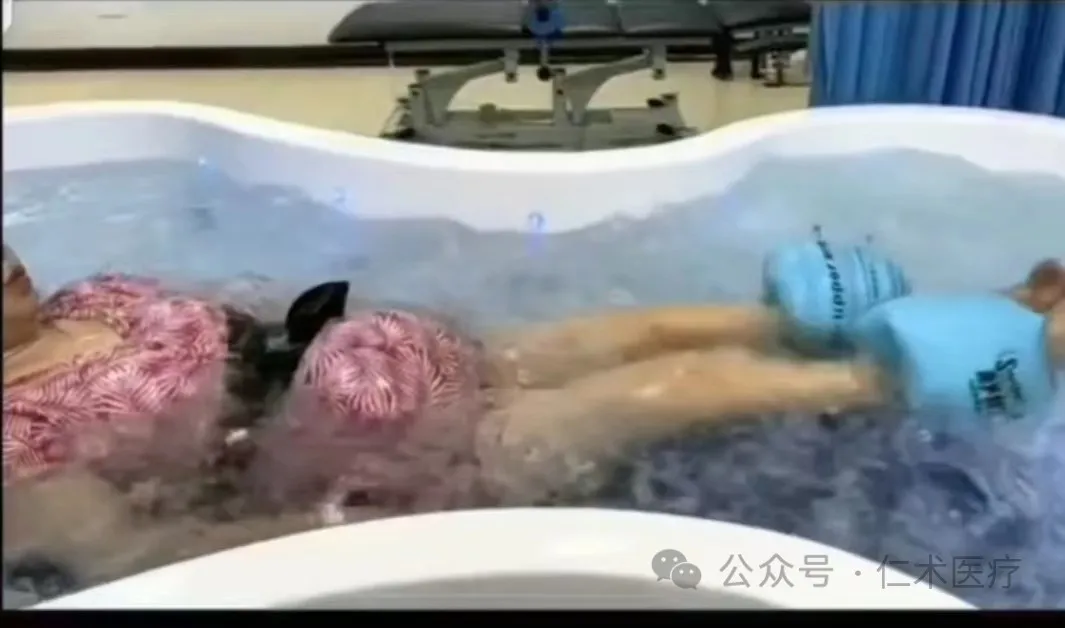
1. Patient Posture The patient floats in the water in a fully supine position with the aid of a swimming circle at the neck and pelvis.
2. Technical Method-The interactive exercise therapy of trunk extension with rotation and trunk flexion with rotation introduced in Bad Ragaz technology is very effective in activating trunk flexor and extensor muscles, which is an improved method of PNF technology.
3. Technical Method 2 This method requires a set of double-pole system. The height of the double-pole is level with the horizontal surface, and the depth of the water should ensure that the patient can fully extend the trunk and limbs without touching the bottom of the swimming pool.

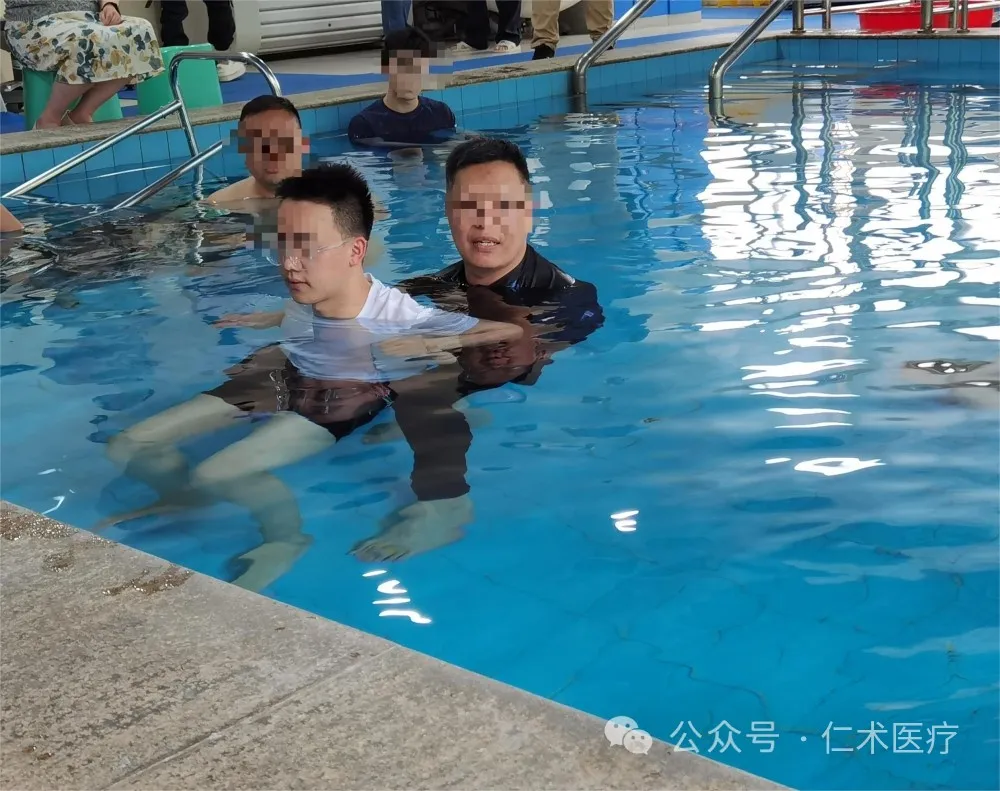
(iii) Balance and balance response training
1. Seat balance training
(1) Patient posture 1: The patient's bilateral shoulder joints are below the horizontal plane, his elbows are straight, his shoulders are flexed forward, his hips, knees and ankles are flexed to 90 degrees as much as possible, and his feet are the same width as his hips.
(2) Technical method 1. The spa therapist stands behind the patient and stabilizes the patient's waist. At first, the therapist gently shakes behind the patient, and the patient uses the head, shoulders, arms, and hands to try to maintain a stable sitting position. The physical therapist is required to assess the amount of disturbance acting on the patient and record the patient's disturbance site. The greater the amount of interference, the more balance and coordination is needed to maintain. The therapist exerts interference in different directions around the patient, and the different directions of the interference also make the patient need to pay more effort to control the body posture.
(3) Patient posture II. The patient sits on a chair without backrest and armrest in the pool, and the horizontal plane is flat with the two shoulder joints.
(4) Technical Method 2: Before the training begins, the therapist should take a sitting or kneeling position in front of the patient to prevent the patient from falling down, thereby helping the patient to improve the confidence of the training. When the patient's confidence increases, the therapist should change the position and stand behind the patient. The therapist tilts the chair sideways, forward, and backward, and encourages the patient to prevent imbalance by adjusting the position of the head and torso. To increase the difficulty of the training, the therapist can create fluctuations in the water flow around the patient to disturb the patient's balance and encourage the patient's head, trunk and lower limbs to take appropriate responses

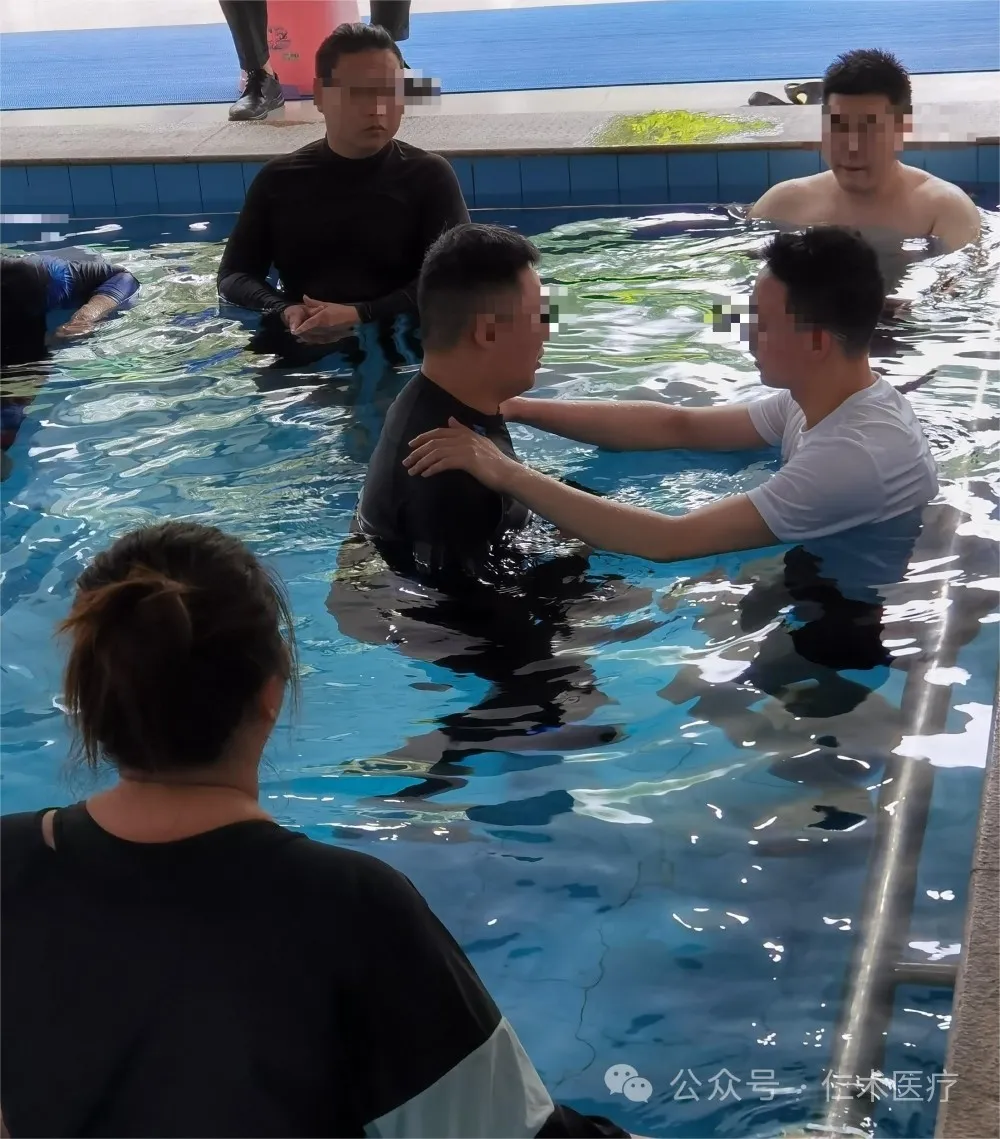
2. Standing balance training
(1) Patient posture 1: The patient is away from the edge of the swimming pool. At this time, the depth of the water should be deep enough to reach the level of the xiphoid process, and the legs should be wide enough to provide the patient with a wide basal surface, which is convenient to provide the patient with more Lateral stability.
(2) Technical method 1: At the beginning, the therapist should stand in front of the patient to operate. After the patient's confidence is improved, the therapist should stand behind the patient. Then the therapist, such as sitting balance training, creates fluctuations in the water flow around the patient. A small amount of fluctuation requires the patient's static balance ability to maintain. When the amount of interference fluctuation increases, more balance and coordination ability is needed to maintain the posture. At this time, the patient's feet can be brought together to further reduce the size of the patient's supporting surface to improve the difficulty of training.
(3) patient posture two: patients like the above training, the starting position to take a standing position, and maintain a wide support base surface.
(4) Technical Method 2: At the beginning, the therapist stands in front of the patient to operate. After the patient's confidence is improved, the therapist stands behind the patient. The therapist then begins to disrupt the patient's balance by moving the patient's pelvis with their hands in different directions. The speed of the beginning of the passage is slow. After the patient's balance response ability is improved, the speed of the passage can be improved. The patient should adjust the position of the whole body by adjusting the position of the shoulder joint, so as to produce balance and balance response.

Related News